IPTV Tutorial – What Is IPTV (Internet Protocol Television)
IPTV Tutorial
Internet Protocol Television ( IPTV)
The conventional television content distribution uses satellite, cable and terrestrial broadcast system formats. But the Internet Protocol TV or IPTV provisions the broadcast of the television series by using the Internet via Internet Protocol (IP) networks.
Internet Protocol TV is very popular nowadays because of its features that allow the subscribers to watch not only the TV shows on their favorite channels but also live broadcasts of their favorite shows, movies, live games like cricket, football, etc and even watching backdated shows of one’s favorite programs.
What Is IPTV?
The internet protocol television can be defined as the broadband media that provisions multimedia services in the form of television, audio, video, graphics, etc. distributed over the internet protocol networks directed to provide the desired QoS, security and reliability of the substance.
The IPTV has come out as the most efficient mode of transmission of television programs. Usually, it works on a request basis and broadcasts only the program that is requested by the subscriber. Whenever you alter your channel, it will transmit a new series of a stream for the viewer.
On the other hand, in the conventional mode of transmission of TV programs, all the channels are broadcasted simultaneously.
Its use is not only limited to Internet television but it is most extensively used in the high-speed subscriber based telecommunication networks for accessing the channels into the customer end by using set-top boxes and routers.
Thus, nowadays it can be watched on PC, laptop and even on smartphones if you have a broadband connection to access its services.
Types Of Internet Protocol Television
1) Live Television: Live broadcast of television or live streaming videos/audio/games etc. with minimum latency like watching a live cricket match, live football, watching reality game shows finale, etc. in real-time as when it is happening.
2) Digital Video Recorder (DVR) or Time-shifted television: It permits watching TV shows that were originally broadcast a few hours back or some days back and replay of current ongoing shows.
The users can view their favorite shows later and even if they miss the broadcast of them due to lack of time at the time of telecast on TV.
3) Video on Demand (VOD): Each user will have a collection of different media files that are stored in his/her device and one can browse and watch them anytime just by selecting them. This feature of Internet Protocol TV uses the real-time streaming protocol for transmission as it deploys unicast mode of transmission.
The IPTV has come out as the most efficient mode of transmission of television programs. Usually, it works on a request basis and broadcasts only the program that is requested by the subscriber. Whenever you alter your channel, it will transmit a new series of a stream for the viewer.
On the other hand, in the conventional mode of transmission of TV programs, all the channels are broadcasted simultaneously.
Its use is not only limited to Internet television but it is most extensively used in the high-speed subscriber based telecommunication networks for accessing the channels into the customer end by using set-top boxes and routers.
Thus, nowadays it can be watched on PC, laptop and even on smartphones if you have a broadband connection to access its services.

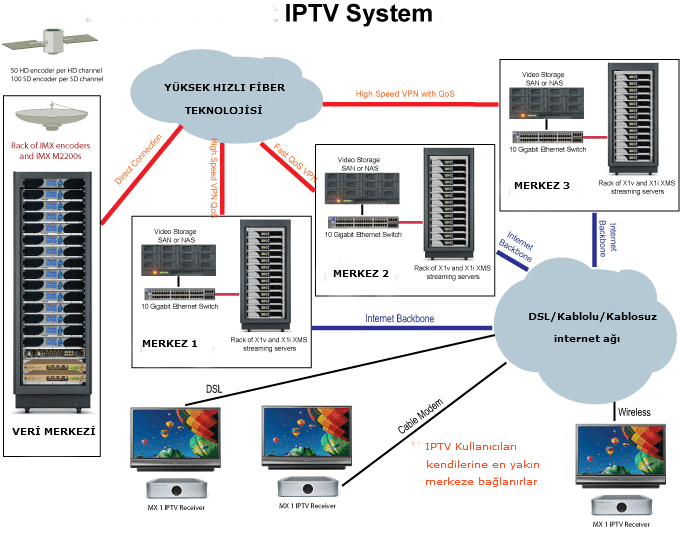
Architecture Of IPTV
The architecture of IPTV comprises four main blocks that are a super head-end, video serving office, local end office, and subscriber’s home.
Functions Of Super-head End
The super-head end wing will download and store all the programs that are broadcast on the national channels of TV on a day-to-day basis.
Then the content of the programs is processed in such a way so that they can be transmitted over the high-velocity internet links like DSL and FTTH links. For the distribution of the IPTV channels, the different multicast IP addresses are used.
The super-head end will float the content to the local office ends by using the multi-program transport stream to the video or data nodes of the far end. The head end acquires the video from various sources and also uses a MPEG encoder and media streamer for delivering the data content.
The head end also provisions the content security by using the conditional access system (CAS) and digital rights management (DRM) system.
Role Of Video Serving Office End
This will combine and store the local content, video on demand and advertising server within it. It can also broadcast the content by using the wireless antenna as well as the high-speed IP links to the zonal end offices.
Role Of Local Office End
The main component at the local end offices is the DSLAM (digital subscriber line access multiplexer) whose main task is to merge the data and the telephony services with the IP video services.
Now the main function of the local end office is to combine all this information and distribute it to the subscriber’s area by using the digital subscriber line (DSL) links or STM links. The DSL will also work as the splitter as it will change the format of the content in the form that can be accessed and required by the end-user.
Subscriber’s End
This can be understood by the example that if the end-user wants the content in the data format then the DSL modem is used to convert the IP data into the format that is compatible with the laptop or desktop. To extract the video content, The STB (set-top box) that makes it compatible to be used on a TV set is deployed.
As the video server networks will utilize huge bandwidths to store and broadcast the stored and on-demand videos, to make optimum use of the bandwidth deployed to these networks, and two architecture models are suggested.
Architecture Models
- First is a centralized architecture model, in this model all the content is stored at one centralized server and it is a good solution to deliver small web-series and small VOD contents.
- The other one is a distributed architecture model, where the content is distributed between the various nodes in a network and distinctive bandwidth is allocated to them as per the requirement of the network.
The distributed architecture is a bit complex but it is effective to deliver a large amount of content over large networks that are used with big service providers.

Architecture Of IPTV

The architecture of IPTV comprises four main blocks that are a super head-end, video serving office, local end office, and subscriber’s home.
Functions Of Super-head End
The super-head end wing will download and store all the programs that are broadcast on the national channels of TV on a day-to-day basis.
Then the content of the programs is processed in such a way so that they can be transmitted over the high-velocity internet links like DSL and FTTH links. For the distribution of the IPTV channels, the different multicast IP addresses are used.
The super-head end will float the content to the local office ends by using the multi-program transport stream to the video or data nodes of the far end. The head end acquires the video from various sources and also uses a MPEG encoder and media streamer for delivering the data content.
The head end also provisions the content security by using the conditional access system (CAS) and digital rights management (DRM) system.
Role Of Video Serving Office End
This will combine and store the local content, video on demand and advertising server within it. It can also broadcast the content by using the wireless antenna as well as the high-speed IP links to the zonal end offices.
Role Of Local Office End
The main component at the local end offices is the DSLAM (digital subscriber line access multiplexer) whose main task is to merge the data and the telephony services with the IP video services.
Now the main function of the local end office is to combine all this information and distribute it to the subscriber’s area by using the digital subscriber line (DSL) links or STM links. The DSL will also work as the splitter as it will change the format of the content in the form that can be accessed and required by the end-user.
Subscriber’s End
This can be understood by the example that if the end-user wants the content in the data format then the DSL modem is used to convert the IP data into the format that is compatible with the laptop or desktop. To extract the video content, The STB (set-top box) that makes it compatible to be used on a TV set is deployed.
As the video server networks will utilize huge bandwidths to store and broadcast the stored and on-demand videos, to make optimum use of the bandwidth deployed to these networks, and two architecture models are suggested.
Architecture Models
- First is a centralized architecture model, in this model all the content is stored at one centralized server and it is a good solution to deliver small web-series and small VOD contents.
- The other one is a distributed architecture model, where the content is distributed between the various nodes in a network and distinctive bandwidth is allocated to them as per the requirement of the network.
The distributed architecture is a bit complex but it is effective to deliver a large amount of content over large networks that are used with big service providers.
Bandwidth Requirement
The IPTV bandwidth requirement for access link is 4 MBPS per channel for SDTV and 20 MBPS for HDTV per channel. For a video-on-demand, the bandwidth requirement is 25 MBPS for high definition video quality.
IPTV Set-top Box (STB)
- The function of the STB is to convert the amenable incoming signal into the video signal which the user can watch on their televisions with the support of the HDMI cable or AV cable or nowadays even with Wi-Fi connection.
- The one end of the STB is connected to the TV while the other end is connected with the internet via a router or modem using the RJ45 connector cable which provisions the high-speed internet connectivity to home premises.
- The set-top box has other many ports and characteristics, but here we need not discuss all of them as they all are not relevant.
- The set-top box can be connected with the tablet or smartphones easily by using LTE Wi-fi networks.


Protocols Used In Internet Protocol TV
IPTV carries both the video on demand (VoD) service which is a unicast and live TV which is a multicast service. To watch these applications the broadband fixed or wireless IP network is connected via embedded OS devices like tablets, smartphones, game consoles, PC and set-top boxes.
To watch these services the video compression is done by H.263 or H.264 generated codec and audio compression is performed by MDCT generated codec and after this encapsulation is done by using MPEG transport stream or RTP packets for a telecast of live and stored VoD services.
Now the protocols used are as below:
- For the service provider based video streaming the IGMP protocol is used. It is also used for changing the live streaming channel from one channel to another. The routing in the network is done by protocol-independent multicast (PIM), which performs the distribution of TV channels from source to the destination customer end who wants to view the content.
- The real-time transport protocol (RTP) via UDP is used to view on-demand content. The encapsulation method deployed here is the H.222 transport stream over TCP.
- For the web-based unicast and multicast live watching RTP via TCP or UDP is used by deploying RTSP over TCP for set-up and control purposes.
- To watch the local content by connecting TV via set-top-box and playing the game online the UPnP AV via HTTP over TCP or UDP is used.
Hybrid IPTV
Due to the increase in demand for watching online video sites such as YouTube, the common satellite and cable TV operators should come out with some solution that will maintain their business by allowing the users to watch Internet-based video along with TV channels on the television sets.
Along with this the pay-TV operators also want them to deliver the required service without adding additional cost and infrastructure to their respective networks.
To meet up the requirements of the users as well as the pay-TV operators the Hybrid IPTV is a good solution. It is a combination of the conventional broadcast TV services with the video on demand based on IP networks.
A hybrid set-top box permits the content from various sources like cable and satellite broadcast channels to be merged with the video content that is to be delivered on the IP networks over an Ethernet connection on the device.
Now the television customer can view both the TV channels and the video content from a wider range of available content without the need for any extra infrastructure.
With the hybrid IPTV set-top boxes one can also access several advanced types of services like repeating a TV show, online gaming, shopping, online batting, watching live games and e-governance, etc. on the television set itself.
As a TV operator, the providers have the option to grant access to various services as mentioned above to the consumers as per the requirement and request of the user to enable or disable the service. This provides flexibility without any network and service complexity to both the service provider as well as the end-user.
Advantages Of IPTV
- To access the services of IPTV, we are only required to install the IPTV set-top box and we can watch the content, thus it is very economical to use.
- Its newest versions can be accessed easily by using a Wi-fi connection as well. It is not compulsory to use a wired internet connection. It makes it easy to use.
- The Internet Protocol TV is purely digital and thus supports all the latest technology to provide a good QoS.
- Several types of programs can be watched simultaneously on the TV screen and smartphones without any interruption.
- Apart from video-on-demand services, we can also use other services like voice, data, online gaming, real-time batting, and telephone services.
- The programs can be viewed by escaping the advertisements which come in between the TV serials and other programs by forwarding them from the remote. It saves the time of the subscribers.
- The IPTV system is user-friendly and time-efficient as the end-user can watch the shows from the stored server anytime they want and can view it according to their choice by using fast-forward, rewind, and pause & play buttons.
Limitations Of Internet Protocol TV
- There is no guarantee of watching the shows on IPTV without any technical faults i.e. if many users are watching the same show at the same instance of time then the server becomes busy and the end-user will not be able to watch the show on that channel and the channel will display error.
- Sometimes a few channels will take a very long time to play a show and will keep on buffering after every 30 seconds of play. This creates a loss of interest in watching the show in the users if it happens frequently.
- At times it hangs very often due to the synchronization problems between the end-user and video serving office.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned various aspects of the IPTV which is one of the most emerging trends of the industry of communication and entertainment nowadays.